HOW TECHNOLOGY IS CREATING THE HOSPITAL OF THE FUTURE
Whether you are enough of a Trekkie to have been to a Star Trek convention or simply enjoy the show you’ll know that it includes some technology which, when first aired, was impossible to imagine in real life. For example, the replicator which could create and recycle things. And the awesome communicator much used by Spock and Captain Kirk. What does this have to do with hospitals? Well, this demonstrates how quietly technology can creep up on us and then suddenly, it is part of our lives. For example, the communication device we all carry with us and now can’t live without!
However, the future does not just happen on its own; the present needs to have a vision of what the future might be. And within the health sector there is currently an impressive amount of vision.
Technology has been embraced by the medical profession and hospitals are changing as more new technologies are developed and adopted in the hospital environment.
Here are some technologies that are taking us to the next frontier and shaping our future hospitals:
Robotics
Surgical Robots are machines that execute surgical tasks. But they are not autonomous. A (human) surgeon performs the surgery using robotic instruments that they guide via a console. Although tiny wristed instruments move like a human hand, they have a much greater range of motion. The small size of the instruments means surgeons can operate through one (or a few) small incisions, helping with complicated operations by allowing greater precision and flexibility than traditional techniques.
Globally, da Vinci surgical systems is most widely used system in this field.
Artificial Intelligence
 Healthcare use of artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to grow rapidly. Examples of ways that AI could reduce and/or mitigate risk include: helping to detect high risk patients by identifying those in need of medical intervention and triggering alerts to medical staff; and helping to deliver personalised recommended dosages by factoring in the unique body chemistry and associated environmental factors associated with individual patients.
Healthcare use of artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to grow rapidly. Examples of ways that AI could reduce and/or mitigate risk include: helping to detect high risk patients by identifying those in need of medical intervention and triggering alerts to medical staff; and helping to deliver personalised recommended dosages by factoring in the unique body chemistry and associated environmental factors associated with individual patients.
The UK’s Babylon Health has a patient-centered remote consultation service that, through deep learning, can provide users with personalised insights to help them to better understand their health.
3D Printing
Additive manufacturing is where a digital file is used to create physical objects by adding multiple layers – it is more commonly called 3D printing. Since the early 1980s more than a dozen methods or technologies have evolved, with examples of 3D printing in medicine (actual and potential) including: customised implants and prosthetics; organ and tissue manufacturing; personalised medical equipment; anatomical models for education and surgical planning.
California-based Organovo is one of the leaders in the research and development of 3D bioprinting; they have a goal of 3D printing patches made of human tissue for defunct organs and entire organs for transplantation.
 Nanomedicine
Nanomedicine
Nanomedicine applies the tools of nanotechnology to the treatment and prevention of illness. It involves the use of nanoscale materials for the delivery of therapeutics (including vaccines), biomarker discovery, bioimaging and for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
There are a number of start-ups around the world with interesting projects, including Israel’s Vecoy Nanomedicines looking to treat viral infections by administering novel nano-scale virus-traps that capture and destroy viruses.
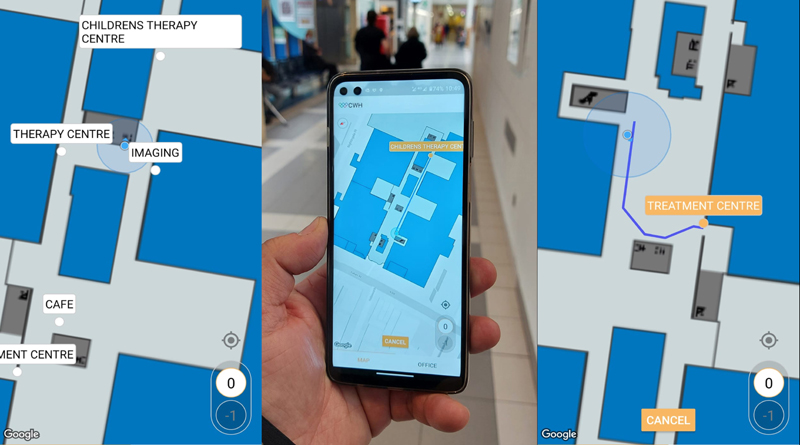
Wayfinding
Wayfinding is an important step forward in making hospitals become more patient-oriented. It also saves the hospital time and money.
 More than 85% of patients ask for directions when they go to a hospital or other public health facility, and 30% of first-time visitors get lost (Source: Deloitte Digital). Wayfinding enables patients and other visitors to navigate from outside the hospital all the way to the specific location they need, whether that is a bed on a ward, a consulting room, the café, or the pharmacy.
More than 85% of patients ask for directions when they go to a hospital or other public health facility, and 30% of first-time visitors get lost (Source: Deloitte Digital). Wayfinding enables patients and other visitors to navigate from outside the hospital all the way to the specific location they need, whether that is a bed on a ward, a consulting room, the café, or the pharmacy.
This saves staff time; many times a day doctors and nurses are stopped (and therefore delayed) by visitors asking for directions; and often patients are late for appointments as they are lost within the hospital. Indoor Wayfinding solves both these problems.
Global positioning systems (GPS) are part of everyday life. We are used to reliable digital navigation outdoors, so it’s an obvious next step to take this navigation indoors.
For example, Buzzstreets technology helps people navigate easier through a hospital as well as giving them a more independent experience. The navigation app can personalise the route, so if you want to avoid the stairs it will show you how, it can also choose the fastest or least busy route for you, plus it can highlight interesting features along the way, for example, it can tell you more about the art you pass. The BuzzStreets system can be found in a few pioneering hospitals, including London’s Chelsea and Westminster Hospital.
Indoor Wayfinding in general has a direct and positive contribution to the experience of patients, visitors and staff.
Just as the writers of Star Trek imagined a handheld mobile phone and something that sounds rather like a 3D printer, we are seeing an imaginative approach to the adoption of new technologies in our hospitals. To take one example, X-ray diagnostics are now supported by machine learning algorithms.
Robert H Goddard, the American physicist and inventor famously said, “It is difficult to say what is impossible; for the dream of yesterday is the hope of today and the reality of tomorrow.” We are seeing the this play out as our hospitals make their visions of the future a reality for their patients.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
 Joe Fernandes, founder and CEO of BuzzStreets, an award-winning navigation platform, that enables organisations (hospitals, shopping malls, airports, offices, stadiums, etc.) to offer their customers an indoor way-finder that allows them to navigate inside the building. The client arrives at the entrance or reception and then uses the bespoke app to navigate to the specific location (room, shop, check-in, office, or even seat) they need. BuzzStreets also supplies movement analytics that can help improve building efficiency and keep track of vital equipment.
Joe Fernandes, founder and CEO of BuzzStreets, an award-winning navigation platform, that enables organisations (hospitals, shopping malls, airports, offices, stadiums, etc.) to offer their customers an indoor way-finder that allows them to navigate inside the building. The client arrives at the entrance or reception and then uses the bespoke app to navigate to the specific location (room, shop, check-in, office, or even seat) they need. BuzzStreets also supplies movement analytics that can help improve building efficiency and keep track of vital equipment.
WEBSITE: www.buzzstreets.com
References:
3D PRINTING
https://www.axial3d.com/blog/beginners-guide-to-medical-3d-printing/
AI
https://healthcareweekly.com/health-technologies/
NANOMEDICINE
https://www.nature.com/subjects/nanomedicine
ORAGNAOVO
https://www.dr-hempel-network.com/digital-health-technolgy/top-10-companies-in-medical-3d-printing/
VECOY
https://www.medicalstartups.org/top/nano/
BABYLON HEALTH
https://medicalfuturist.com/top-artificial-intelligence-companies-in-healthcare/#
BUZZSTREETS
www.buzzstreets.com